
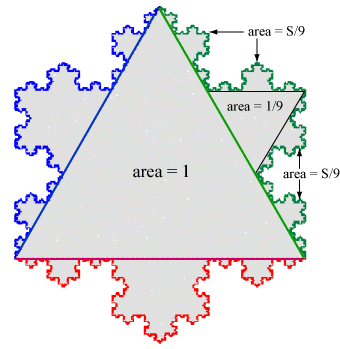
The area of the equilateral triangle inside the green section is the center equilateral triangle scaled by 1/3, so its area is 1/9. Each of the four smaller copies of the green section are a 1/3-scaled version of the entire green section, so each of them has area S/9. Therefore \[S = \frac{1}{9} + 4\cdot\frac{S}{9} \Rightarrow S = \frac{1}{5}.\] The blue and red sections outside the center equilateral triangle but inside the snowflake have the same area as the green section. Thus the area of the Koch snowflake is 1 + 3(1/5) = 8/5.
More generally, the area of the snowflake would be 8/5 times the area of the original equilateral triangle.